In this project, we develop learning-augmented algorithms for a variety of classic online algorithms and apply them to a broad range of applications, including energy optimization, video streaming, electric vehicle charging scheduling, etc.
The Algorithms with Predictions, also known as learning-augmented algorithms or algorithms with ML advice, is an emerging topic at the intersection of theoretical computer science and machine learning. Here are some foundational questions that the research aims to answer:
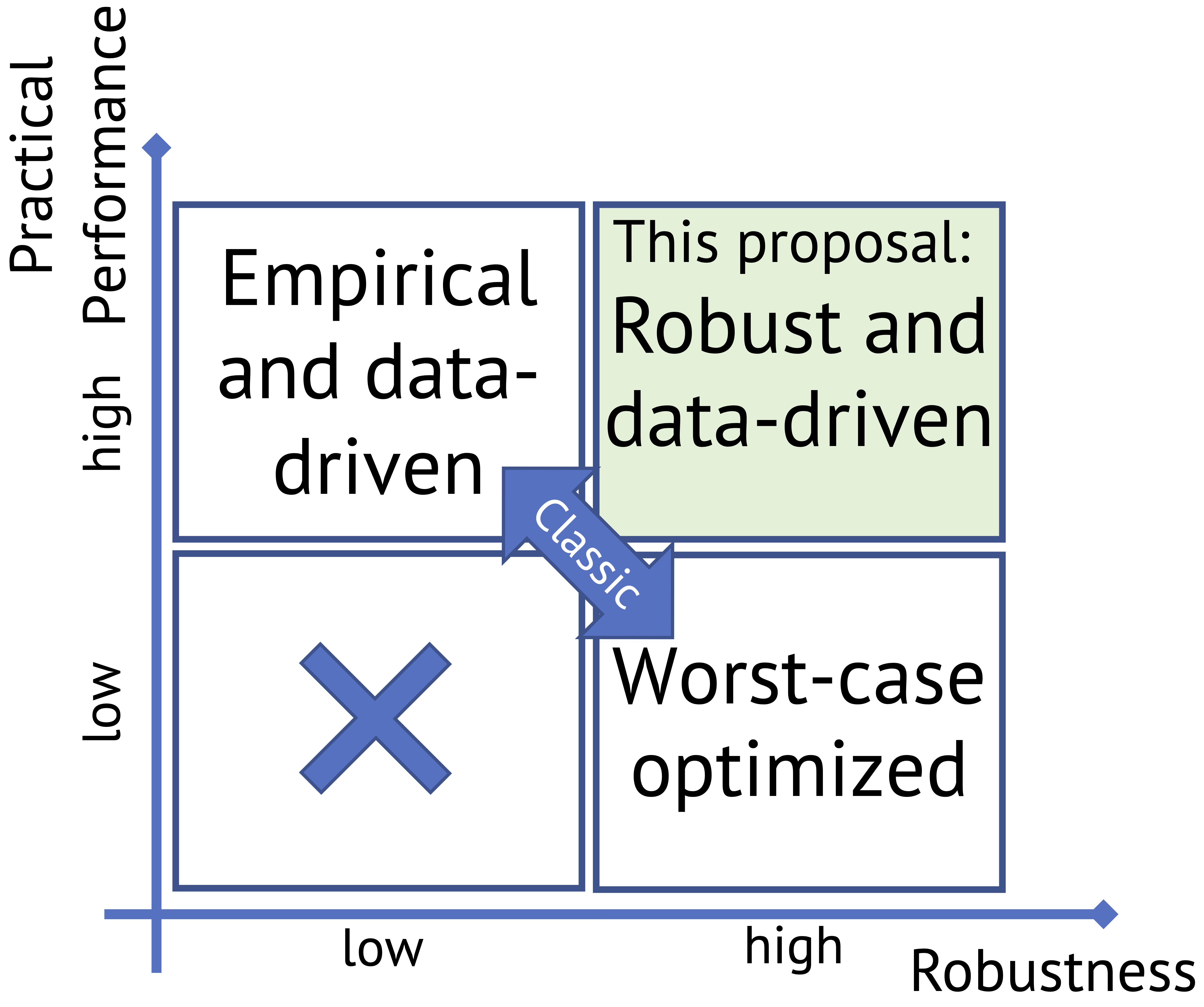
- How to parameterize algorithms so that they can adapt their behavior to the properties of the input distribution and consequently improve their practical performance while still satisfying the theoretical worst-case guarantees.
- How to use imperfect (untrusted) predictions robustly – retaining worst-case guarantees of classic algorithms – yet achieve satisfactory performance when the predictions are accurate?
- How to determine the right time to use advice for online problems when it comes with an additional cost?
Generally speaking, a result in this area takes a problem with strong information-theoretic lower bounds (for instance, on the competitive ratio), identifies a compact prediction that can be learned from real data, and proves the performance of the algorithm to the quality of the underlying prediction. The field has blossomed with applications to a broad range of classic domains in theoretical computer science, such as classical streaming algorithms, online scheduling, clustering, filtering data structures, and many others. The focus of our research in the SOLAR lab is mainly on online algorithms with predictions, including the following problems:
- Online knapsack problem
- One-way trading problem
- Online search problem, a.k.a, k-search (k-min, k-max)
- Online inventory management problem
- The ski-rental problem and applications to energy generation scheduling